Climate knowledge for research and politics
EU project COMFORT starts with strong GEOMAR participation.
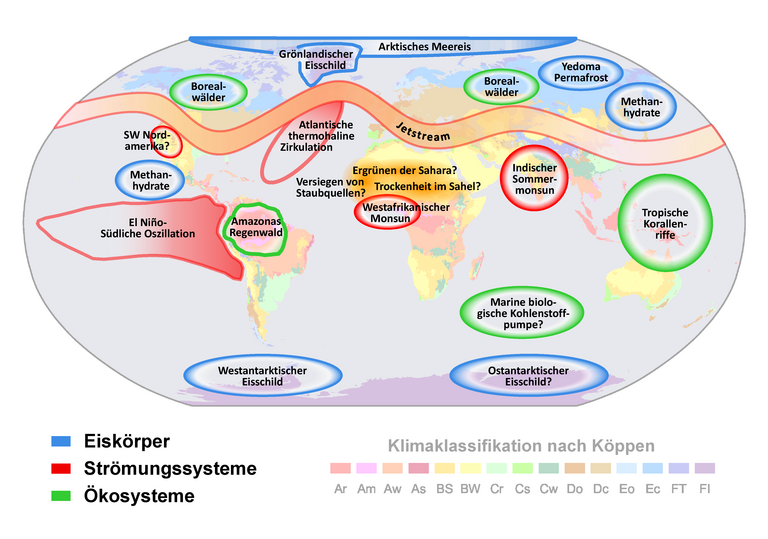
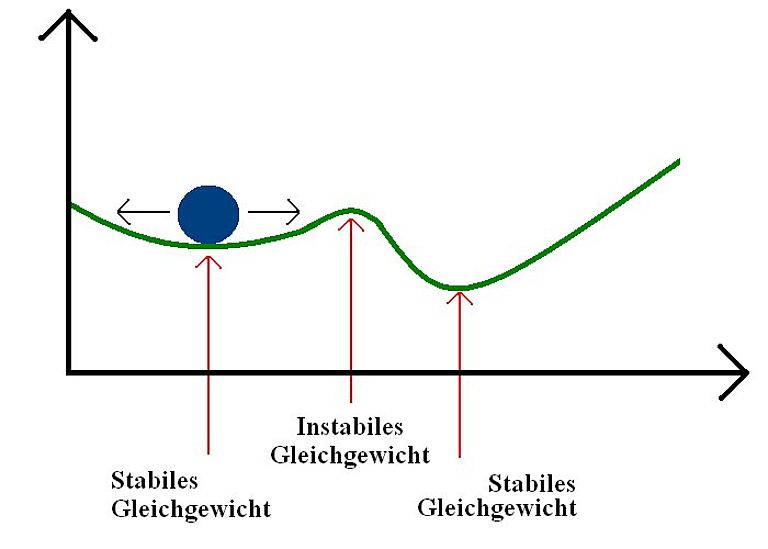
11. October 2019/Bergen, Kiel. Due to human activities, more and more trace gases are released to the atmosphere, leading to global warming in the atmosphere but also to ocean acidification and deoxygenation. This impacts the marine ecosystems, e.g. coral reefs are in danger as the ocean warms and becomes more acidified. Once specific tipping points are passed such species might be irreversibly lost. Due to the complex interactions of different biogeochemical cycles in the ocean and the atmosphere such tipping points are difficult to identify.
The COMFORT research project, funded by the European Union with a total of 8 million euros, will close knowledge gaps on key ocean tipping points within the Earth system. The project focuses on the triple threat of (1) warming, (2) deoxygenation, and (3) ocean acidification, and how to optimally deal with this threat. This week, the COMFORT consortium started its work with a kick-off meeting in Bergen, Norway.
In the COMFORT project, researchers from the fields of Earth System Science, Oceanography, Fisheries Science and Ecology are working together to identify climate-induced ocean tipping points and attribute them to processes, quantify related impacts and establish multi-dimensional safe operating spaces, and provide respective mitigation targets and options, as well as projected mitigation pathways.
The GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel is one of 32 partner institutions from 12 countries. In addition, Dr. David Keller from the GEOMAR research unit "Biogeochemical Modelling" leads the work package “Ocean mitigation options assessment”.
The results of the project will serve as guidelines for policy decisions to prevent dangerous climate change. They will also contribute to future reports of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
Please note:
This project is funded under the European Union's Horizon 2020 Research Framework Programme (grant number 820989).